5195 words, 15 mins
以太坊的加密算法,公私钥生成,椭圆曲线
密码学
区块链的所有数据是公开透明的,并且也没有加密,任何人可以查看链上发生的所有交易。
同时所有的交易也是可以验证的,而链上的数据验证都只需要知道公开的地址,并不需要私钥,这些都是密码学保证的。
密钥及地址
我们从私钥到地址的生成过程来梳理一下相关的名词概念。
1.私钥生成
通过随机函数生成 256 位的数字,这里你要注意,一定要使用安全的随机函数,一定要对你所使用的随机函数有充分的认识。
比如微信小程序就没办法使用安全的随机函数。
私钥一般使用 64 个 16 进制数表示,如下,每一个数字代表了 4 个 bit 位
f8f8a2f43c8376ccb0871305060d7b27b0554d2cc72bccf41b2705608452f315
2.公钥生成
公钥是私钥通过椭圆曲线算法(secp256k1)得到的,具体算法如下
K = k * G
- K 生成的公钥
- k 就是我们的私钥
- G 是一个常量
注意这里的乘法不是简单的数字相乘,也不能用除法反推私钥,他是不可逆的
这里的乘法我们可以转换成多次的加法,也就是K = G + G + G + … + G,G相加k次,他的几何意义是G这个点在椭圆曲线上进行k次用切线获取交点的x轴对称点转换。而一次G+G运算,就是G点得到椭圆曲线的切线,并和椭圆曲线相交得到的R’点,然后得到R’的x轴对称点R点。
3. 演示
我们通过https://andrea.corbellini.name/ecc/interactive/reals-add.html演示一下
P和Q使用同一点(1,2),可以得到R的坐标为(-1, -4)
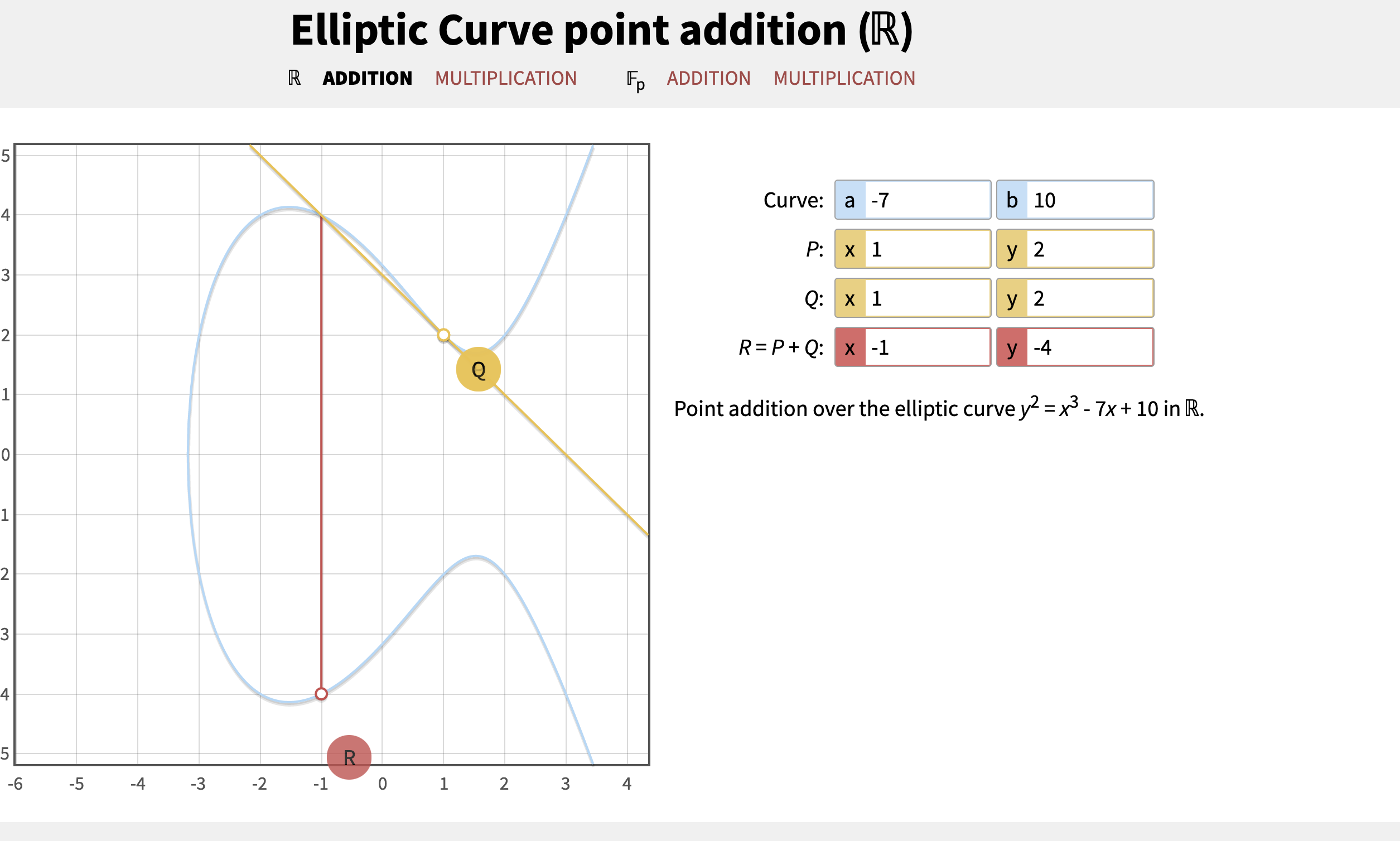
然后我们再用R作为新的P坐标,可以得到R坐标为()
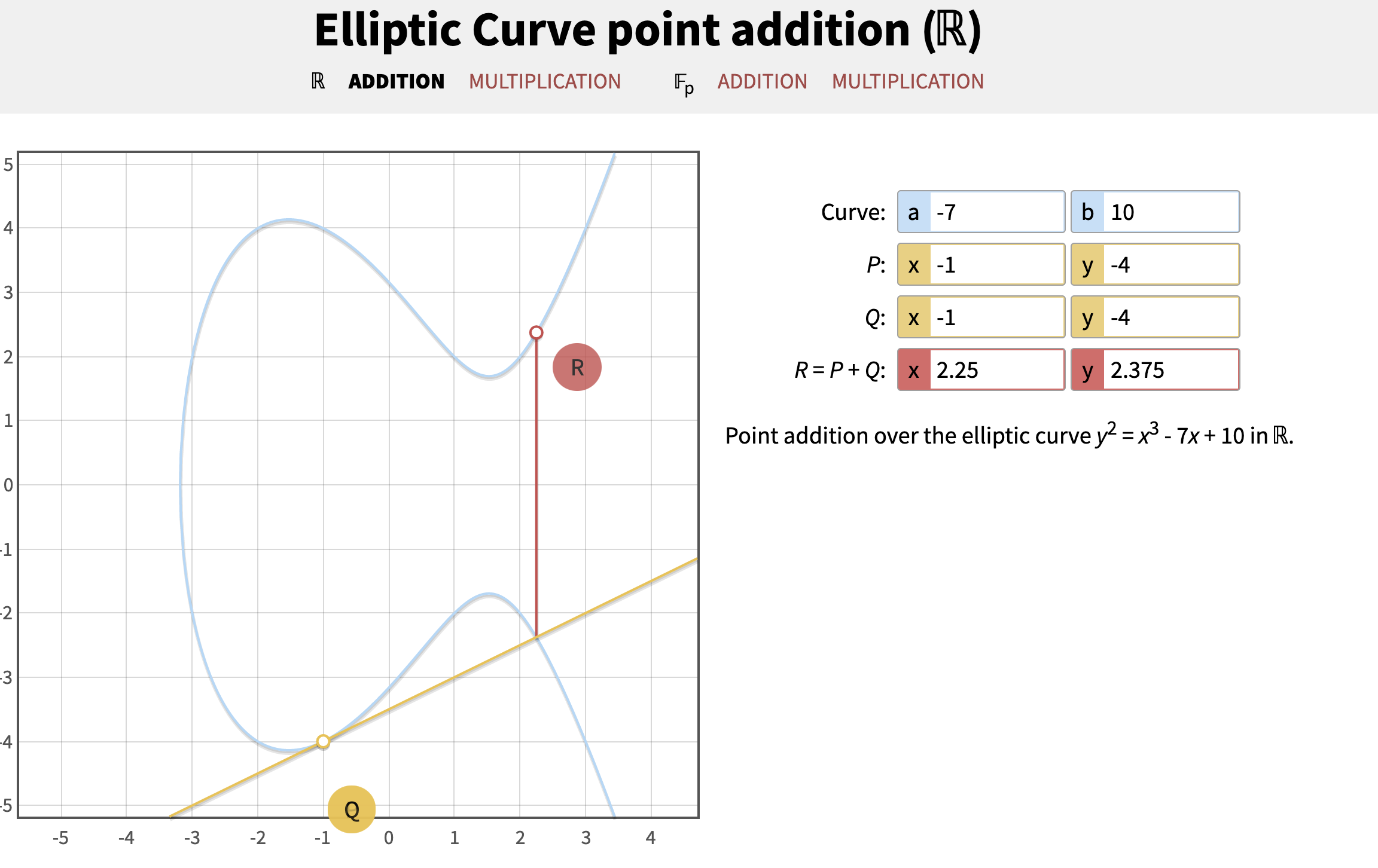
这样不断的循环下去,循环k次,得到最终的坐标点,就是我们的公钥地址坐标点。
例子:
K = f8f8a2f43c8376ccb0871305060d7b27b0554d2cc72bccf41b2705608452f315 * G
得到的公钥坐标为
x = 6e145ccef1033dea239875dd00dfb4fee6e3348b84985c92f103444683bae07b
y = 83b5c38e5e2b0c8529d7fa3f64d46daa1ece2d9ac14cab9477d042c84c32ccd0
最终我们的公钥由前缀04(uncompressed point) + x坐标 + y坐标组成
04 + x-coordinate (32 bytes/64 hex) + y-coordinate (32 bytes/64 hex)
046e145ccef1033dea239875dd00dfb4fee6e3348b84985c92f103444683bae07b\
83b5c38e5e2b0c8529d7fa3f64d46daa1ece2d9ac14cab9477d042c84c32ccd0
4.椭圆曲线的公式
\[y^2 = (x^3 + 7) mod p\]mod p的意义是椭圆曲线所有的坐标都在有限域内, p为
\[p = 2^{256} – 2^{32} – 2^9 – 2^8 – 2^7 – 2^6 – 2^4 – 1\]例子坐标点代入公式,使用irb测试
2.6.5 :004 > p = 2 ** 256 - 2 ** 32 - 2 ** 9 - 2 ** 8 - 2 ** 7 - 2 ** 6 - 2 ** 4 - 1
=> 115792089237316195423570985008687907853269984665640564039457584007908834671663
2.6.5 :005 > x = 49790390825249384486033144355916864607616083520101638681403973749255924539515
=> 49790390825249384486033144355916864607616083520101638681403973749255924539515
2.6.5 :006 > y = 59574132161899900045862086493921015780032175291755807399284007721050341297360
=> 59574132161899900045862086493921015780032175291755807399284007721050341297360
2.6.5 :007 > (x ** 3 + 7 - y**2) % p
=> 0
5. 地址生成
之前得到的公钥地址,可以通hash算法将长度缩短,并且无法反推,这里我们要看下hash算法的特点
- Determinism: A given input message always produces the same hash output.
- Verifiability:Computing the hash of a message is efficient (linear complexity).
- Noncorrelation:A small change to the message (e.g., a 1-bit change) should change the hash output so extensively that it cannot be correlated to the hash of the original message.
- Irreversibility: Computing the message from its hash is infeasible, equivalent to a brute-force search through all possible messages.
- Collision protection:It should be infeasible to calculate two different messages that produce the same hash output.
hash算法的用途有:
- Data fingerprinting
- Message integrity (error detection)
- Proof of work
- Authentication (password hashing and key stretching)
- Pseudorandom number generators
- Message commitment (commit–reveal mechanisms)
- Unique identifiers
以太坊使用的hash算法是: Keccak-256,是修复过安全漏洞的,可以通过对空字符串hash判断是否用的修复过的算法
Keccak256("") =
c5d2460186f7233c927e7db2dcc703c0e500b653ca82273b7bfad8045d85a470 # 修复过的
SHA3("") =
a7ffc6f8bf1ed76651c14756a061d662f580ff4de43b49fa82d80a4b80f8434a
对于上面的例子中得到的公钥
046e145ccef1033dea239875dd00dfb4fee6e3348b84985c92f103444683bae07b\
83b5c38e5e2b0c8529d7fa3f64d46daa1ece2d9ac14cab9477d042c84c32ccd0
注意:生成地址的时候我们不使用0x04前缀
对其hash后得到
const keccak256 = require('keccak256')
console.log(keccak256('0x6e145ccef1033dea239875dd00dfb4fee6e3348b84985c92f103444683bae07b83b5c38e5e2b0c8529d7fa3f64d46daa1ece2d9ac14cab9477d042c84c32ccd0').toString('hex'))
2a5bc342ed616b5ba5732269001d3f1ef827552ae1114027bd3ecf1f086ba0f9
然后只取最后的20个字节作为最终的地址,因为是16进制显示的,一个字符代表4个bit,所以需要40个字符
001d3f1ef827552ae1114027bd3ecf1f086ba0f9
加上前缀0x
0x001d3f1ef827552ae1114027bd3ecf1f086ba0f9
使用代码演示从私钥到公钥及地址的过程
ruby例子:
require 'openssl'
require 'base16'
require 'digest/sha3'
def eth_address(public_key)
s = public_key[2, 128]
s.downcase!
s = Base16.decode16(s)
h = Digest::SHA3.hexdigest(s, 256)
a = '0x' + h[-40..-1]
return a
end
ec = OpenSSL::PKey::EC.new('secp256k1')
ec.generate_key
public_key = ec.public_key.to_bn.to_s(16)
private_key = ec.private_key.to_s(16)
eth_address = eth_address(public_key)
puts "address: #{eth_address}"
puts "private_key: #{private_key}"
puts "public_key: #{public_key}"
运行:
➜ ecc git:(master) ✗ ruby generate_private_key_and_address.rb
address: 0xb1e97939c2942d209b077e5e253eec7b1eb58a7c
private_key: 7CC979D685A6D90A4DD618C524BC71BE11F234B65B0FCD562ED5051DCAD76052
public_key: 04F9EC4283DD66748B616B0471CE49B29F83016E7D330E74A49B7AA9920232498DA45A2BB4320694D889EA87EE3FDA4464C63140217A0DF46A1139B41BA9FE70EA
js例子:
const EthCrypto = require('eth-crypto');
const identity = EthCrypto.createIdentity();
console.dir(identity);
运行:
➜ ecc git:(master) ✗ node generate_private_key_and_address.js
{
address: '0x07f9eEbB50D44887C39d65C58fD68aBe34e6719e',
privateKey: '0x82c0e50caa370abcf93d71e5aa96dc8f106bd5722903d3d89a4934fcc0d80b99',
publicKey: '272eeebcc2ddfc1da82f6707dc2c048d04b499de0883f6f1895769836c0b50749002d78c292c3eaaecc7e253ec1381e6d5b1c026cbbc37dfd8a9af5c78a70b26'
}
可验证正确性的地址
以太坊的地址本身没有CheckSum,也不区分大小写,为了增加安全性,EIP-55提出了如何使用大小写敏感的地址格式来验证其正确性
具体步骤如下:
1. 对小写的地址进行hash
Keccak256("001d3f1ef827552ae1114027bd3ecf1f086ba0f9") =
23a69c1653e4ebbb619b0b2cb8a9bad49892a8b9695d9a19d8f673ca991deae1
2. 得到的hash值和原小写地址进行一一对比
Address: 001d3f1ef827552ae1114027bd3ecf1f086ba0f9
Hash : 23a69c1653e4ebbb619b0b2cb8a9bad49892a8b9...
每一个地址中的字母,如果hash对应的值大小>=0x8,则应该为大写
比如第四个是字母d,但对应的是6,所以小写
第六个字母是f,对应的是c,所以大写
最终得到的是
Address: 001d3F1ef827552Ae1114027BD3ECF1f086bA0F9
Hash : 23a69c1653e4ebbb619b0b2cb8a9bad49892a8b9...
而一旦我们没有使用正确的地址格式,我们对其hash后,再进行验证就会出错
可使用https://github.com/miguelmota/ethereum-checksum-address测试,web3也有相应的方法